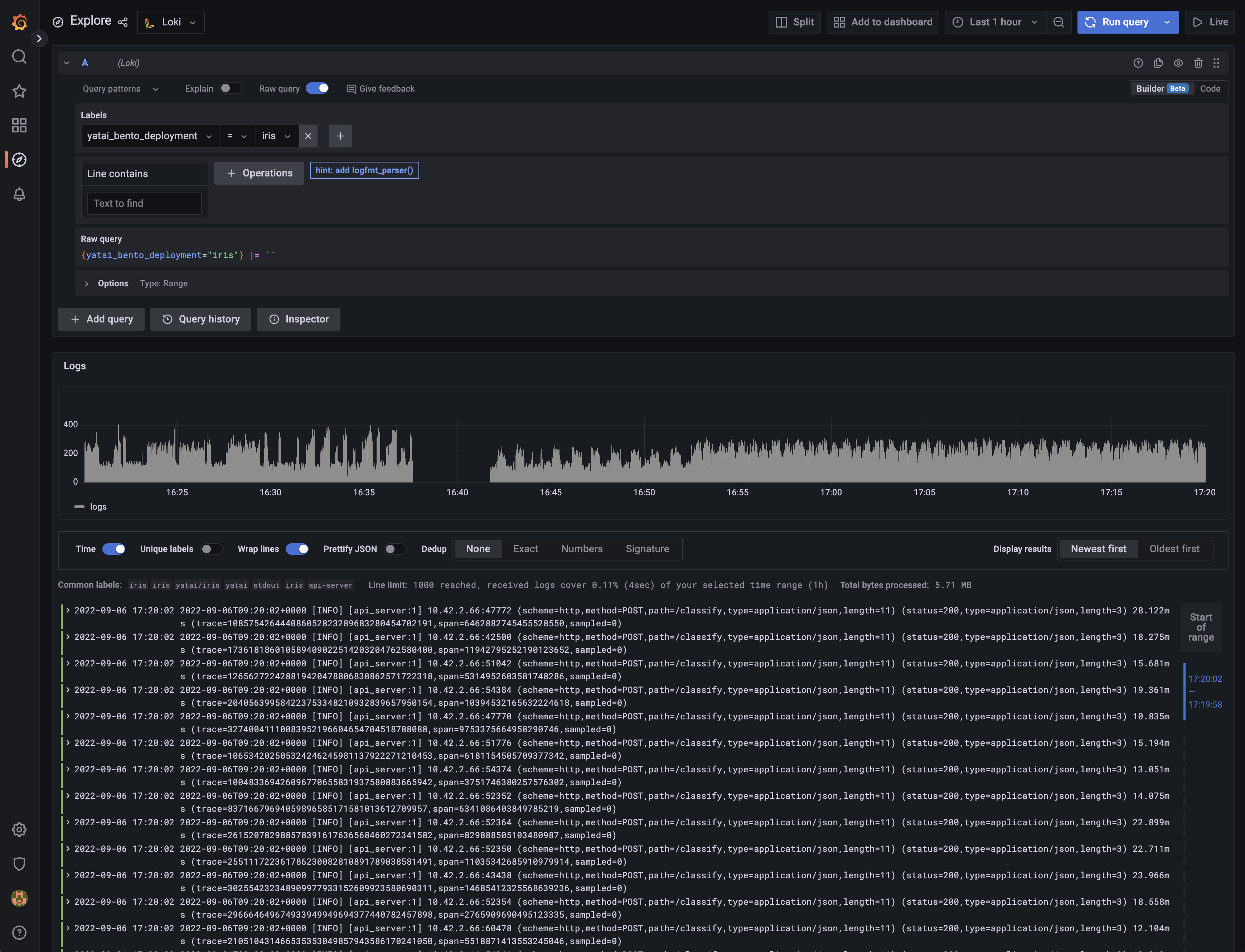
Collecting Logs¶
Yatai supports using Loki to collect, store and query BentoDeployment’s logs
Note
This documentation is just for BentoDeployment logs, not for Yatai itself.
Prerequisites¶
yatai-deployment
Because the metrics collected are related to BentotDeployment, it relies on yatai-deployment
Kubernetes
Kubernetes cluster with version 1.20 or newer
Note
If you do not have a production Kubernetes cluster and want to install yatai for development and testing purposes. You can use minikube to set up a local Kubernetes cluster for testing.
Dynamic Volume Provisioning
As Loki requires log storage, you need to enable dynamic volume provisioning in your Kubernetes cluster. For more detailed information, please refer to Dynamic Volume Provisioning.
Helm
We use Helm to install Loki Stack.
Quick setup¶
Note
This quick setup script can only be used for “”development”” and “”testing”” purposes
This script will automatically install the following dependencies inside the yatai-monitoring namespace of the Kubernetes cluster:
MinIO
Promtail
Loki
bash <(curl -s "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bentoml/yatai/main/scripts/quick-setup-yatai-logging.sh")
Setup steps¶
1. Create a namespace for Logging Stack¶
kubectl create ns yatai-logging
2. Install MinIO¶
1. Create MinIO Tenant¶
Create a MinIO Tenant
export S3_ACCESS_KEY=$(LC_ALL=C tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 20)
export S3_SECRET_KEY=$(LC_ALL=C tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 20)
kubectl create secret generic yatai-logging-minio \
--from-literal=accesskey=$S3_ACCESS_KEY \
--from-literal=secretkey=$S3_SECRET_KEY \
-n yatai-logging
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: minio.min.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
labels:
app: minio
name: yatai-logging-minio
namespace: yatai-logging
spec:
credsSecret:
name: yatai-logging-minio
image: quay.io/bentoml/minio-minio:RELEASE.2021-10-06T23-36-31Z
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
mountPath: /export
podManagementPolicy: Parallel
pools:
- servers: 4
volumeClaimTemplate:
metadata:
name: data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
volumesPerServer: 4
requestAutoCert: false
s3:
bucketDNS: false
subPath: /data
EOF
Install the
minio-operatorhelm chart
helm repo add minio https://operator.min.io/
helm repo update minio
export S3_ACCESS_KEY=$(LC_ALL=C tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 20)
export S3_SECRET_KEY=$(LC_ALL=C tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 20)
cat <<EOF > /tmp/minio-values.yaml
tenants:
- image:
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
repository: quay.io/bentoml/minio-minio
tag: RELEASE.2021-10-06T23-36-31Z
metrics:
enabled: false
port: 9000
mountPath: /export
name: logging-minio
namespace: yatai-logging
pools:
- servers: 4
size: 20Gi
volumesPerServer: 4
secrets:
accessKey: $S3_ACCESS_KEY
enabled: true
name: yatai-logging-minio
secretKey: $S3_SECRET_KEY
subPath: /data
EOF
helm install minio-operator minio/minio-operator -n yatai-logging -f /tmp/minio-values.yaml
Verify the
minio-operatorinstallation
Monitor the minio-operator components until all of the components show a STATUS of Running or Completed. You can do this by running the following command and inspecting the output:
kubectl -n yatai-logging get pod -l app.kubernetes.io/name=minio-operator
Expected output:
Note
You need to be patient for a while until the status of all pods becomes Running
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
minio-operator-console-9d9cbbcc8-flzrw 1/1 Running 0 2m39s
minio-operator-6c984995c9-l8j2j 1/1 Running 0 2m39s
2. Verify the MinIO tenant installation¶
Monitor the MinIO tenant components until all of the components show a STATUS of Running or Completed. You can do this by running the following command and inspecting the output:
kubectl -n yatai-logging get pod -l app=minio
Expected output:
Note
Since the pods are created by the minio-operator, it may take a minute for these pods to be created. You need to be patient for a while until the status of all pods becomes Running
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
yatai-logging-minio-ss-0-0 1/1 Running 0 143m
yatai-logging-minio-ss-0-1 1/1 Running 0 143m
yatai-logging-minio-ss-0-2 1/1 Running 0 143m
yatai-logging-minio-ss-0-3 1/1 Running 0 143m
3. Prepare S3 connection params¶
export S3_ENDPOINT=minio.yatai-logging.svc.cluster.local
export S3_REGION=foo
export S3_BUCKET_NAME=loki-data
export S3_SECURE=false
export S3_ACCESS_KEY=$(kubectl -n yatai-logging get secret yatai-logging-minio -o jsonpath='{.data.accesskey}' | base64 -d)
export S3_SECRET_KEY=$(kubectl -n yatai-logging get secret yatai-logging-minio -o jsonpath='{.data.secretkey}' | base64 -d)
4. Test S3 connection¶
kubectl -n yatai-logging delete pod s3-client 2> /dev/null || true; \
kubectl run s3-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' \
--namespace yatai-logging \
--env "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$S3_ACCESS_KEY" \
--env "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$S3_SECRET_KEY" \
--image quay.io/bentoml/s3-client:0.0.1 \
--command -- sh -c "s3-client -e http://$S3_ENDPOINT listbuckets && echo successfully"
The output should be:
Note
If the previous command reports an error that the service has not been initialized, please retry several times
successfully
pod "s3-client" deleted
3. Install Loki¶
1. Install Microservices mode Loki¶
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update grafana
cat <<EOF | helm upgrade --install loki grafana/loki-distributed -n yatai-logging --version 0.65.0 -f -
loki:
image:
registry: quay.io/bentoml
repository: grafana-loki
tag: 2.6.1
structuredConfig:
ingester:
# Disable chunk transfer which is not possible with statefulsets
# and unnecessary for boltdb-shipper
max_transfer_retries: 0
chunk_idle_period: 1h
chunk_target_size: 1536000
max_chunk_age: 1h
storage_config:
aws:
s3: http://$S3_ACCESS_KEY:$S3_SECRET_KEY@$S3_ENDPOINT/$S3_BUCKET_NAME
s3forcepathstyle: true
boltdb_shipper:
shared_store: s3
schema_config:
configs:
- from: 2020-09-07
store: boltdb-shipper
object_store: s3
schema: v11
index:
prefix: loki_index_
period: 24h
gateway:
image:
registry: quay.io/bentoml
repository: nginxinc-nginx-unprivileged
tag: 1.19-alpine
EOF
2. Verify the Loki installation¶
kubectl -n yatai-logging get pod -l app.kubernetes.io/name=loki-distributed
Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
loki-loki-distributed-gateway-548dd9b7f7-sw246 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
loki-loki-distributed-query-frontend-6988cd4b8b-72qrh 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
loki-loki-distributed-distributor-5778bc756b-ldbc2 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
loki-loki-distributed-querier-0 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
loki-loki-distributed-ingester-0 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
4. Install Promtail¶
1. Install Promtail helm chart¶
cat <<EOF | helm upgrade --install promtail grafana/promtail -n yatai-logging --version 6.6.1 -f -
config:
clients:
- url: http://loki-loki-distributed-gateway.yatai-logging.svc.cluster.local/loki/api/v1/push
tenant_id: 1
snippets:
pipelineStages:
- docker: {}
- cri: {}
- multiline:
firstline: '^[^ ]'
max_wait_time: 500ms
extraRelabelConfigs:
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_yatai_ai_bento_deployment
target_label: yatai_bento_deployment
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_yatai_ai_bento_deployment_component_type
target_label: yatai_bento_deployment_component_type
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_yatai_ai_bento_deployment_component_name
target_label: yatai_bento_deployment_component_name
EOF
2. Verify the Promtail installation¶
kubectl -n yatai-logging get pod -l app.kubernetes.io/name=promtail
Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
promtail-kqnnm 1/1 Running 0 13m
promtail-t76fm 1/1 Running 0 13m
promtail-rrflp 1/1 Running 0 13m
5. Set Loki as the Grafana datasource¶
Note
The following steps are assuming you have already have Grafana installed in your cluster and sidecar.datasources.enabled turned on.
1. Create the Grafana datasource configmap¶
cat <<EOF > /tmp/loki-datasource.yaml
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Loki
type: loki
access: proxy
url: http://loki-loki-distributed-gateway.yatai-logging.svc.cluster.local
version: 1
editable: false
EOF
kubectl -n yatai-monitoring create configmap loki-datasource --from-file=/tmp/loki-datasource.yaml
kubectl -n yatai-monitoring label configmap loki-datasource grafana_datasource=1
2. Restart the Grafana pod¶
kubectl -n yatai-monitoring rollout restart deployment grafana
Make sure the Grafana pod is restarted successfully:
kubectl -n yatai-monitoring get pod -l app.kubernetes.io/name=grafana
6. View the logs in Grafana¶